Types of refractory bricks
Currently, the most common classification of refractories is the chemical composition classification, which can be divided into silica, aluminosilicate, magnesium, dolomite and carbon composite refractories.
1.Silica Refractories
Silica refractory is a refractory material with SiO₂ as the main component and SiO₂ mass fraction not less than 93%, which can be either a definite or indefinite refractory material. The refractories have the advantages of high thermal conductivity, high load softening point, and strong resistance to acidic slag erosion, but the biggest disadvantage is the low stability of thermal shock resistance. Therefore, this refractory is mainly used as structural materials for coke ovens, glass melting kilns, acid steel furnaces and other thermal equipment.
2.Aluminosilicate refractories
Aluminosilicate refractories are refractories with AI₂O₃ and SiO₂ as main components. According to the different content of AI₂O₃ in the refractories can be divided into semi-siliceous (mass fraction 15%~30%), clayey (mass fraction 30%~48%) and high-alumina (mass fraction >48%) refractories. The refractories have the advantages of light weight, thermal stability, and good heat preservation performance, but their starting deformation temperature is 1400℃. Therefore, aluminosilicate refractories are generally used as heat preservation materials in the metallurgical industry and are not used in the working layer.

3.Magnesium refractories
Magnesia refractories are refractories with magnesite as the main crystalline phase and MgO mass fraction greater than 80%. Influenced by the composition of magnesium raw materials, the main components of magnesium refractories are MgO, FeO, Fe₂O₃, AI₂O₃, SiO₂, CaO, Cr₂O₃.The melting point of MgO is as high as 2,800 ℃, and the refractoriness of magnesium refractory materials reaches 2,000 ℃, so that the magnesium refractories have a good high-temperature resistant performance. Magnesium refractories include magnesium bricks, magnesium olivine refractories, magnesium-aluminum spinel refractories, magnesium-chromium refractories and alabaster refractories. Among them, magnesium-chromium refractories are made of magnesium sand and chromite and have magnesium sand as the main component. Compared with traditional magnesium bricks, magnesium-chromium refractories are more thermally stable and are widely used in non-ferrous smelting furnaces. However, since hexavalent chromium is a serious hazard to the environment and human health, especially to water, it is necessary to strictly control the alkaline medium and oxygen partial pressure in the production and fabrication process.

4.Dolomitic refractories
Dolomitic refractories are alkaline refractories with dolomite as the main raw material and MgO and CaO as the main components, of which the mass fraction of CaO is 40%~60% and the mass fraction of magnesium oxide is 30%~40%. The refractory temperature of dolomitic refractories is above 1780℃, and the softening start temperature of 0.2MPa load is 1550℃, which shows that it has good high temperature stability. Dolomitic refractory belongs to strong alkaline refractory, which has strong slag resistance to alkaline slag, but poor slag resistance to acidic slag. Therefore, this refractory material is mainly used in flat furnace wall and bottom, rotary kiln firing belt, etc.
5.Carbon composite refractories
Carbon composite refractories, also known as carbon-containing refractories, is a multi-phase composite refractories made of two or more different properties of refractory oxides (MgO, CaO, Al₂O₃, ZrO₂, etc.) and carbonaceous materials and non-oxidizing materials as raw materials, and carbonaceous materials as a binding agent. Carbon composite refractories have high refractoriness, good thermal and electrical conductivity, excellent load deflection temperature and high-temperature strength, and better resistance to slagging and thermal shock than other refractories, but this class of products have the disadvantage of easy oxidation. Therefore, this refractory material is mainly used in the field of smelting stainless steel, pure steel and low-sulfur steel and other high-quality steel.
Selection of refractories for side-blast furnaces
1.Side Blowout Furnace Introduction
Side-blowing furnace is a smelting equipment for producing crude copper, oxygen-rich air is drummed into the furnace through the secondary air outlet set in the slag line area, and the reaction is carried out under the action of high temperature, the crude copper is sunk into the lower part of the melting pool and discharged to the electric furnace, while the slag is gathered in the upper part of the melting pool and discharged to the electric furnace through the overflow, and the reaction gas is discharged to the boiler process gas from the flue.
The structure of the side-blast furnace is a fixed rectangular furnace, which is made of copper water jacket, refractory material and steel structure. The furnace body is divided from bottom to top into four parts: furnace cylinder, furnace body, furnace roof and flue. The cylinder for storing the crude copper and slag produced by the reaction is made of refractory bricks, and a slag chamber is set up at the end of the cylinder for copper-slag separation. Furnace body is divided into reaction area and flue gas area, reaction area consists of copper water jacket and 1 air outlet, flue gas area consists of slotted copper water jacket and 2 air outlets for slag protection. Reaction flue gas is discharged from the water jacket into the flue. The flue space size is calculated according to the flue gas flow rate to ensure that the flue gas in the flue residence time of more than 2s. The main reaction area of the side-blowing furnace belongs to the protective position of the copper water jacket, and the refractory material is mainly used in the furnace cylinder, slag room and flue.
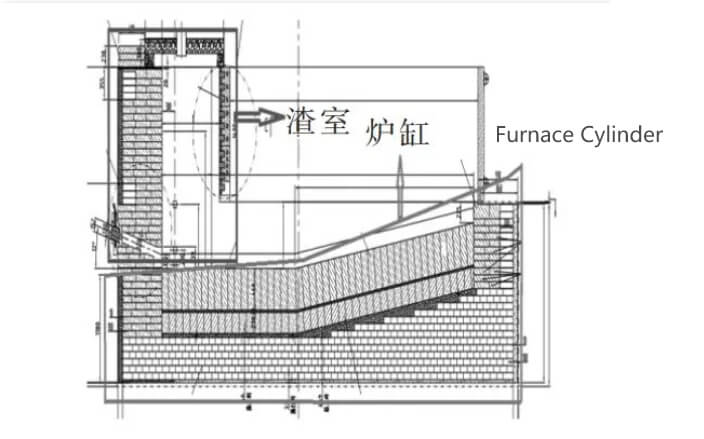
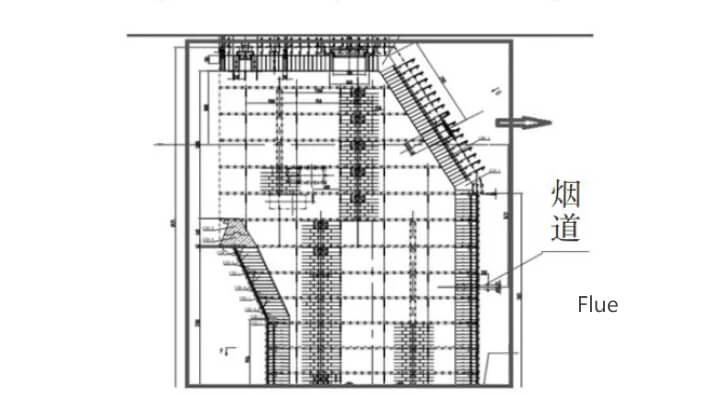
2.Selection of refractory compositions for side-blast furnaces
From the working principle of the side-blowing furnace can be seen, the side-blowing furnace cylinder, slag chamber will be subject to melt erosion and scouring, the flue will be a small amount of slag spray irrigation erosion and dusty flue gas scouring. Under normal furnace conditions, the temperature of these three areas is 1100~1300℃; but in the case of furnace instability, the temperature of these three areas can reach 1400℃ or more. In the actual production process, the side-blowing furnace needs to be supplied into the oxygen-enriched 1 wind and 2 winds, and the formation of a strong oxidizing atmosphere in the local area, so the side-blowing furnace should be selected not easy to be oxidized refractory bricks. The main components of slag are FeO, SiO₂, CaO, AI₂O₃, high-alumina refractories and silica refractories will be involved in slagging, which is not suitable for side-blowing furnace. Therefore, side-blowing furnace refractories need to have high temperature resistance, high thermal stability, high load deflection temperature, high compressive strength, oxidation resistance, and do not participate in slagging. Combined with the characteristics of the refractory material, the side-blowing furnace should choose magnesium refractory material. Increasing the content of Cr₂O₃ in magnesium refractories can improve the resistance to slag erosion of the material, so the refractory bricks of the side-blowing furnace cylinder, slag chamber and flue are chosen to be magnesium-chromium refractory materials with higher Cr₂O₃ content.
3.Selection of refractory bonding forms for side-blast furnaces
According to the magnesium-chromium refractory materials, including direct bonding, semi-recombined, electrofusion re-combined magnesium-chromium refractory materials. Among them, the direct combination of magnesium-chromium refractories is a high-purity sintered magnesium sand and chromite as raw materials, will be fused magnesium sand and chrome ore direct sintering; half re-combination of magnesium-chromium refractories are fused magnesium-chromium sand as a genus, adding part of the chrome ore and magnesium sand or sintered magnesium-chromium synthetic material for fine powder, high-temperature sintering from the fusion; fusion and then combined magnesium-chromium refractory materials are chromium ore and fused magnesium sand in the electric furnace electric melting, to obtain the electrofusion of magnesium-chromium sand, and then Sintered at high temperature.
The performance of electrofusion rebonded MgCr refractory is the best, and the performance of semi-rebonded MgCr refractory is the second best. Combined with the side-blowing furnace cylinder, slag chamber and flue area on the loss of refractory materials, the cylinder, slag chamber, flue area, respectively, the use of semi-bonded, electrofusion re-bonded, direct bonded magnesium-chromium refractories.
The service life of refractory material directly affects the production operation rate and production cost, and it is necessary to choose the appropriate type of refractory material and combination method for the working environment in different areas, which is the most effective means to improve the service life of refractory material.
