The composition of refractory materials in the tundish and the refractory damage problems that occur in daily work are analyzed one by one from the aspects of refractory design, use and management, the causes are found and solutions are proposed to ensure the safe use of refractory materials.
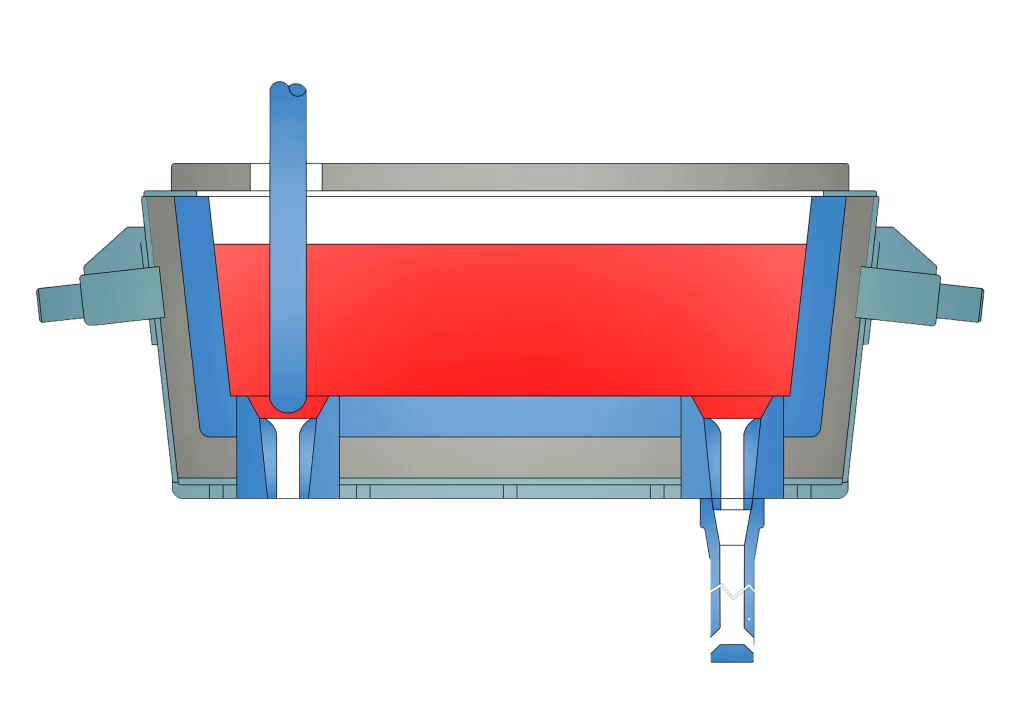
In continuous casting operations, the tundish is used for the retention and transfer of molten steel. The molten steel from the ladle is retained, calmed and kept warm here, and finally distributed to the crystallizer one by one through the water inlet in the tundish to complete the conversion of molten steel to steel billet. The part of the tundish that contacts the high-temperature molten steel is mainly refractory materials, and its quality directly determines the life of the tundish and the quality of the molten steel. For different smelting processes, the configuration and requirements of refractory materials in the tundish are also different.
1.Tundish refractory composition
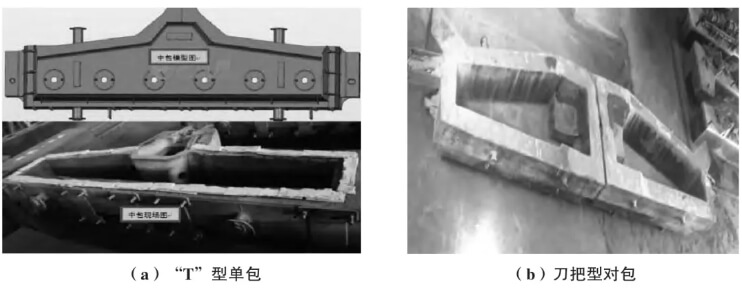
The interior of the tundish is composed of high temperature resistant materials. Different smelting processes require different tundish shapes and different refractory configurations. The commonly used tundish shapes are “T”-shaped single tundish and knife-handle-shaped double tundish, as shown in Figure 1. The internal refractory configuration is designed with different materials according to the use requirements of the tundish and the particularity of the smelting steel. Generally, the permanent layer is cast with castables, and the working layer is formed by vibrating and ramming magnesium dry materials.
Conventional intermediate package contained in the steel, the capacity is generally 20% to 40% of the steel package, the body shell from the steel plate welding assembly, package lining by the combination of refractory materials.
The composition of the refractory material in the intermediate package. Mainly includes intermediate ladle body, intermediate ladle cover, control of steel flow rate of the plug bar [some are with the slider (also known as the lower water mouth) to control the flow], steel flow through the water mouth [upper water mouth seat brick, upper water mouth, lower water mouth (also known as the slider), immersed in the water mouth]. The connection area between the ladle and the intermediate ladle is connected using a large ladle protection sleeve. Liquid steel flows out of the bottom of the ladle and into the intermediate ladle through the ladle protection casing, also known as protection pouring, and some companies do not use the ladle protection casing, commonly known as bare pouring. In the intermediate package in order to cope with the liquid steel from a certain height flow down to the bottom of the package resistant material damage caused by the liquid steel is set up directly below the impact area, the use of impact plate or flow stabilizer resistant material, accept the liquid steel initial strong impact.
2.The vulnerable parts and reasons of refractory materials in tundish (without plug flow control)
In the process of using the intermediate packages of the pair pack type, the areas that are generally prone to accidents are: the intermediate package slag line area, around the impact zone, and the upper water outlet.
2.1 Intermediate package slag line parts
The dry material at the slag line of the tundish is not resistant to erosion and scouring by molten steel, especially when production is unstable, there is a low liquid level pouring phenomenon on site, the slag line position changes, and the accident of steel leakage occurs, as shown in Figure 3.
The main reason is that the refractory material in the tundish is not baked properly, especially in winter, the moisture in the gas is not completely removed, the baking time is short, and the strength of the dry material in the working layer of the tundish does not reach the required strength.

2.2 Around the impact zone of the tundish
The guard plate around the impact area of the middle ladle of the ladle type is easy to fall off and collapse, which leads to the erosion of the permanent layer of liquid steel and the occurrence of steel leakage through the ladle.
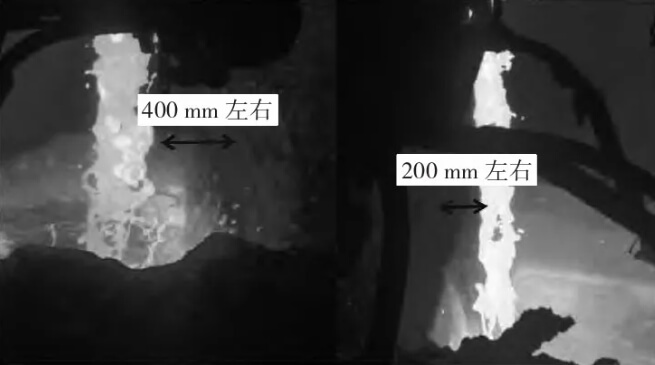
The main reason is that when the steel liquid of the ladle is initially poured, the position of the ladle and the intermediate ladle is not centered, resulting in the two water outlets of the ladle and the impact zone of the intermediate ladle are not centered, resulting in the steel liquid being biased towards the position of one of the intermediate ladle’s shielding plate, resulting in the shielding plate being damaged, collapsed, and flaked off. Figure 4 shows the situation that the steel flow is not centered at the early stage of pouring without the use of large packet protection casing at the site.
2.3 Tundish water inlet
The service life of the upper water outlet of the intermediate package is short. The main reason is that in the process of gradually increasing production at the site, the zirconium core inside the spout is not resistant to steel scouring, and the diameter expansion is serious, resulting in reddening of the lower spout, leakage through the packet, and accidents through the packet.
3.Measures to address the problem
3.1 Baking of intermediate packages
The baking of the tundish is divided into offline baking and online baking, all of which use conventional blast furnace gas burners. On-site offline baking (with mold) is shown in Figure 6: There is a baker on the tundish. During normal combustion, the gas enters from the middle nozzle on the upper part of the burner, and the air (oxygen) enters from the side nozzle to ensure complete combustion of the gas. According to the flame combustion situation, adjust the ratio of gas and air (oxygen) at any time, lengthen the burning flame, and descend to the bottom of the tundish to bake the bottom of the tundish. The normal baking time is about 2 hours. In winter, according to the hardening degree of the dry material and the size of the flame, the baking time can be appropriately extended to 3 to 4 hours.

In the middle packet continuous casting platform baking (line baking), in accordance with a certain baking system, specifically according to the packet type, the material configuration is different and take different baking system. First of all, the intermediate packet of debris and water in the mouth of the debris cleaned up, from the site under the water mouth observation, the intermediate packet of flame downstream to the water mouth for the best,as shown in Figure 7.

Some enterprises, according to the site conditions, use an inverted suction device from the lower water outlet to suck down the flame in the intermediate packet, so that the flame and heat in the intermediate packet fully reaches the lower water outlet; some enterprises directly install the immersed water outlet, combined with the inverted suction device to suck down the flame in the intermediate packet, and then reach the immersed water outlet via the upper water outlet and the lower water outlet.
For intermediate bale baking (using blast furnace gas), the key management points are as follows:
(1) Clean the residue in the intermediate package and the water outlet before baking to ensure that the water outlet can be effectively baked.
(2) Check whether the pressure of various gas sources (gas, compressed air) of the roaster reaches the specified pressure and whether various meters are intact.
(3) Use an open flame against the nozzle of the roaster, or place firewood to burn in the middle bag, open the gas main valve, air valve, gas sub-valve in turn, ignite each gas burner in sequence, adjust the air-gas ratio, so that the gas is fully combusted.
(4) During the baking process, the workers should always stand in the upwind position to monitor and observe the burning condition of the burners at any time, if there is flame out, turn off the gas in order, then close the sub-valves, find out the reason, and then start from the above steps to re-light the fire.
The baking of blast furnace gas can be carried out in three stages, and the baking time is controlled above 5 h. The specific baking standards are as follows:
Stage 1: Bake on low heat (<800°C) for >120 min (can be extended as needed).
The second stage: small fire heating to medium fire (800 ~ 1,000 ℃) more than 60 min.
The third stage: large fire baking (1,000 ~ 1,050 ℃) more than 90 min can be poured steel.
The following precautions should be taken during the baking process:
(1) In principle, the baking time of large fire is not more than 6 h, because at this time, the dry material strength is low, the thermal expansion is large, and the bag may collapse. According to the actual situation on the spot, after the large fire baking can not be changed to small fire baking repeatedly, otherwise it is easy to cause the dry material to produce cracks and embrittlement.
(2) When the temperature rises too fast from small fire to medium fire, due to the gas in the packet wall can not be effectively excluded, it will make the packet wall to produce large cracks and separation of serious, serious separation of the intermediate packet in the use of the packet can be caused by the collapse of the packet and the reduction of the strength of the overall quality of refractory materials.
(3) In the fire baking, the package wall produces a slight separation phenomenon (less than 20 mm) does not affect the normal use. The ratio of wind and gas should be strictly controlled while baking.
3.2 Intermediate packet water outlet improvement
The short service life of the intermediate packet water spout is mainly due to the poor impact resistance of the aluminum and carbon material outside the zirconium core of the intermediate packet water spout, and the erosion resistance of the zirconium core and the aluminum and carbon material outside the zirconium core decreases after the increase of the flow rate of steel after the increase of the pulling speed in continuous casting (the diameter of the upper and lower water spouts expands at the same time). According to the site conditions, the zirconium core outside the intermediate packet water outlet was improved, mainly by improving the material, improving the compressive strength, and improving the impact resistance of the aluminum carbon material outside the zirconium core water outlet; at the same time, the zirconium core inside the water outlet was improved by enlarging the outer diameter of the zirconium cores inside the water outlets of the upper and lower water outlets by 10 to 20 mm.
After the improvement, the service life of the upper spout of the intermediate package was improved, and the reddening phenomenon of the lower spout no longer occurred.
3.3 Strengthening the day-to-day management of intermediate packages
(1) According to the working conditions of the intermediate ladle used to choose the appropriate intermediate ladle refractory, for smelting ordinary steel, choose long-life refractory, improve the service life of the intermediate ladle, reduce the cost of the process; for smelting special steel, the use of special refractory, you can choose the age of the economic ladle, to improve the cleanliness of the steel, and to improve the quality of the molten steel.
(2) The intermediate ladle should be clean and tidy without debris. For the cold shrinkage cracks produced during the offline baking process, the construction of coating materials can be used to rectify the situation.
(3) for the use of knife handle type to the package of the intermediate package, the general use of the bottom of the package impact plate, the side of the use of the guard plate, the formation of a pouring area, here in the middle of the package pouring by the liquid steel impact is the largest, usually choose corundum mullite or silicon carbide refractory, etc.; for the “T” type of single packet is generally used in the form of a flow stabilizer, usually choose the High-aluminum mullite refractory material.
(4) intermediate package in the use of the process needs to carry out the whole process of supervision and management, for the large package casting steel flow must be adjusted at any time when the large package rotary table, to ensure that the steel flow is centered, to avoid steel scouring the impact area of the refractory, resulting in excessive erosion of the guard plate, the life of the reduction. For the intermediate package in the use of various abnormalities in the process, timely analysis and adjustment.
(5) Do a good job in the use of intermediate packet cards and records, to facilitate the analysis and summary of the intermediate packet off the line.
For the steelmaking process in the steel enterprise, continuous casting operation system in the intermediate package casting process of high consumption of refractory material, need to improve the number of multi-furnace continuous casting to consider, while the use of new technologies, the selection of cost-effective refractory manufacturers; further study of the intermediate package casting system of refractory material erosion mechanism, to find out the erosion of its parts of the law, to improve the use of continuous casting refractory conditions, improve its service life in order to reduce costs, and to improve safety production factor and product quality of steel. Eventually improve the safety production factor and steel product quality.