Heating furnace is a thermal equipment used to heat steel billets or small ingots during steel rolling or forging, and its operating temperature is generally 1300~1400℃. With the large-scale and high-efficiency of rolling mills, higher requirements are put forward for heating furnaces. Its development trend is large-scale, low-consumption, pollution-free and automated operation, and the furnace building materials have also undergone major changes.
1.Refractory materials for furnace body
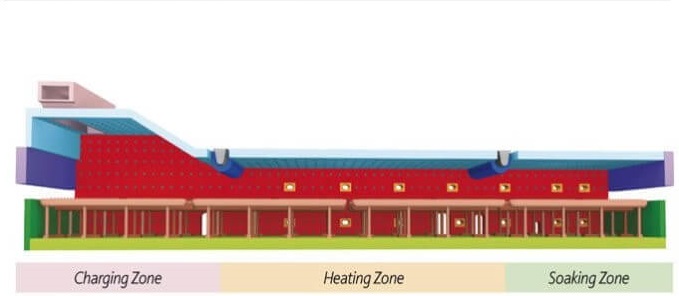
The furnace body consists of a furnace wall, a furnace bottom and a furnace roof. An end burner is installed on one end wall of the furnace, and there is a discharge door on the end wall of the soaking section, and a feed door on the other end wall. In addition to the furnace door and manhole on the side wall, a side burner is sometimes installed on the side wall of the heating section; the bottom of the push-steel furnace is composed of a soaking bed and a water-cooled pipe slide or ceramic slide bricks, and the bottom of the walking furnace is composed of a fixed beam (bottom) and a walking beam. The furnace bottom is usually referred to as a solid furnace bottom made of brick or amorphous refractory materials. The furnace roof is divided into two types: arched roof and flat roof. The furnace top is affected by factors such as high temperature, airflow scouring and thermal stress, especially the furnace top of the front part of the heating section and the soaking section, which is more easily damaged and is the weak link of the entire furnace body. Therefore. The life of the furnace top represents the service life of the heating furnace.
(1) Brick-built furnace body. The furnace lining is built with insulation bricks and refractory bricks. The insulation layer of the furnace is built with clay or high-alumina insulation bricks, floating bead bricks, diatomaceous earth bricks and refractory fiber felt, with a thickness of 113 to 300 mm. The working layer of the furnace wall is built with clay refractory bricks with a thickness of 230 to 400 mm. The openings can be built with brick arches, special-shaped bricks or covered with long strips of clay refractory bricks. If the furnace wall is high, high-alumina tensile bricks should be installed at appropriate intervals to prevent the furnace wall from tipping over. At the same time, the bottom of the furnace wall in the heating section needs to be thickened to increase its stability. The furnace wall is more easily damaged by the collision of steel billets. The furnace wall around the burner and the side outlet, etc., is most easily damaged by high temperature, rapid cooling and heating, and mechanical effects.
The working layer thickness of the furnace bottom is 300-400mm. The preheating section is built with clay refractory bricks, and the heating section is built with clay or high-alumina refractory bricks. A layer of metallurgical magnesia sand is laid on it to resist the erosion of iron oxide slag. Magnesia bricks or magnesia-chrome bricks can also be used to directly build a protective layer. The solid bottom soaking bed of the soaking section is damaged quickly due to high temperature and billet impact, moving wear and slag erosion. When high-alumina bricks or magnesia bricks are used as the working layer of this part, the service life is about half a year. If fused mullite bricks or corundum bricks are used instead, the service life can be extended to about 1 year. When the furnace roof is a brick arch, the working layer thickness is 230-300mm, and a 120-300mm thick insulation brick insulation layer is added. When a suspended flat roof is used, the working layer thickness is 230-250mm, and the insulation layer thickness is about 70mm. The hanging bricks used for hanging flat roofs are divided into single groove type, single-sided groove type, double-sided groove type and clamping type. Generally, soil hanging bricks are used, and high-aluminum hanging bricks are also used in high-temperature areas. The special-shaped hanging bricks commonly used in the furnace roof pressing part do not need to be insulated. The service life of the clay refractory brick furnace roof is 1 to 2 years, and the life of the high-aluminum brick furnace roof is slightly higher. After the fired bricks are replaced with unfired high-aluminum hanging bricks, the service life can be increased by about 1 times. Under normal operation, the service life of the rolling steel heating furnace is generally 1 to 3 years. Due to intermittent operation, the forging steel heating furnace is subject to greater thermal stress and mechanical collision, and its service life is 3 to 11 months.
(2) Prefabricated blocks are hoisted into the furnace body. Prefabricated blocks are made of refractory castables such as aluminate cement, phosphate low cement and water glass. If clay is combined with refractory castables to make prefabricated blocks, anchor bricks must be provided. The prefabricated blocks on the furnace roof are divided into two types: arched and long strips. If reinforced steel bars are used, they must be placed in the non-working layer.
(3) Refractory plastic ramming furnace body. The working layer of the furnace lining with anchors is made by ramming refractory plastic. The gaps between anchor bricks or hanging bricks need to be filled with refractory plastic blanks and compacted with a pneumatic hammer or a tamping machine. Refractory plastic including the furnace bottom is generally constructed in layers and sections, and the surface is shaved, vent holes are punched, and expansion joints are cut. The advantages of refractory plastic furnace lining are strong integrity, good sintering properties and high high temperature strength. Therefore, the furnace lining generally does not peel off and has a service life of about 13 years.
(4) Lining castables are used to pour the furnace body. The working layer of the furnace lining is poured on site with refractory castables. The structure of the furnace wall and the top is the same as that of the refractory plastic furnace body. After the anchor bricks or hanging bricks are installed in place, the refractory castable mixture is laid from one side, and then vibrated and compacted with a vibrator (paddle). Continuous construction and timely maintenance should be carried out. Before 1980, high-alumina cement or phosphate refractory castables were generally used to pour the furnace lining working layer, but the furnace lining working layer in the high-temperature area is prone to structural peeling, affecting its use. The service life is generally 2 to 4 years. After 1980, the furnace body is generally poured with various clay-bonded or low-cement series refractory castables. The furnace bottom in the high-temperature area is sometimes poured with slag-resistant corundum, mullite or magnesia-chromium refractory castables, and the soaking bed is poured with wear-resistant heat-resistant steel fiber refractory castables. The furnace baking time is about 8 days. Under normal operation, the service life of a steel rolling heating furnace can reach 4 to 10 years, and the service life of a forging steel heating furnace is 2 to 4 years.
Burner bricks are refractory products used in various burner parts, mainly for organizing flames. Flat flame burners are installed on the furnace roof, and other burners are installed on the furnace wall. The burner bricks are in the shape of a trumpet, consisting of one or several pieces, and are inlaid in the furnace lining. The center must be aligned with the center of the burner to ensure effective mixing and preheating of fuel and air, organize the flame shape and stabilize the combustion process. The bricks and the surrounding linings are often subjected to high temperature, sudden temperature changes and air flow scouring. They are damaged quickly. The service life of clay burner bricks used for burning gas is about 1 year, and when heavy oil is used as fuel, its life is only 3 to 6 months. When high-alumina or sillimanite burner bricks are used instead, the use effect is improved; the burner bricks made of high-alumina cement or phosphate refractory castables on gas-fired heating furnaces have a life of 1 to 2 years. Burner bricks made of corundum or mullite low-cement refractory castables are used on oil-fired heating furnaces, and the life span is 6 months to 3 years.
2.Refractory materials for combustion chamber
Heating furnaces used for burning coal are divided into various types such as reciprocating grate type and cyclone combustion type, and are generally composed of bottom, wall and top parts. The lining of ordinary combustion chambers is usually built with clay bricks or high-alumina bricks. Due to the high operating temperature and large temperature fluctuations, slag erosion and mechanical damage during slag cleaning, its life is about 1 year. When refractory castables such as special high-alumina clinker, corundum, mullite or magnesia-aluminum spinel are used to cast the lining, the integrity is good and the slag is not sticky, and the service life can be extended to 1 to 3 years. The lining of the cyclone combustion chamber is cast with high-strength and high-thermal conductivity silicon carbide refractory castables, and the service life is 1 to 2 years. The waist furnace is the passage between the combustion chamber and the furnace of the heating furnace. The operating temperature is about 1600℃. When it is built with sillimanite bricks or corundum bricks, its life is only about 0.5 years.
3.Refractory materials for furnace doors and steel spouts
Used to close the holes on the furnace wall, there are two types: side-opening type and lifting type. Furnace doors are generally lined with clay bricks, refractory castables or refractory plastics, high-alumina insulation bricks or refractory fiber felt and other materials; side-opening furnace doors can be used for one furnace service, and lifting furnace doors are affected by factors such as temperature fluctuations and mechanical collisions, and their service life is about 1 year.
The steel spout is used in the heating furnace for side discharge of steel billets. Except for water-cooled cast iron steel spouts, high-aluminum bricks or magnesia bricks are generally used for masonry, with a service life of 3 to 6 months. When sintered or fused mullite bricks are used for masonry, they have high strength and good wear resistance, but poor thermal shock resistance and are prone to cracking, with a service life of about 1 year. The integral steel spout is cast on site using heat-resistant steel fiber reinforced corundum refractory castables, with a service life of more than 2 years.

4.Refractory materials for ceramic slides
Small push-steel heating furnace, with a ceramic slideway composed of brown corundum-silicon carbide slideway bricks, and 2 or 4 rows of base walls are built with refractory bricks in the length direction of the furnace. High-aluminum silicon carbide seat bricks are built on the base wall, and then the slideway bricks are installed to form a ceramic slideway. The steel billet moves on the slideway to achieve heating on both the upper and lower sides, with the advantages of low energy consumption and no black marks on the steel billet. The ceramic slideway is subjected to high temperature, steel billet load, high temperature wear and iron oxide slag erosion, etc., and the use conditions are relatively harsh, and its life is about 1 year.
5.Refractory materials for insulation of furnace bottom water cooling pipes
For large and medium-sized pusher steel or walking beam heating furnaces, the water cooling pipes at the bottom of the furnace are composed of thick-walled water cooling pipes distributed longitudinally and transversely and supporting. The purpose of insulation is to reduce the heat taken away by the cooling medium, reduce the black mark of the steel billet and improve the heating quality. The insulation methods include inlaying special-shaped clay bricks or hanging horseshoe-shaped bricks, welding of welded tile prefabricated blocks made of refractory plastic or refractory castables, and on-site wrapping with the material and refractory fiber felt. The service life is generally 3 to 12 months. The service life is more than 1 year when high-quality refractory plastic, ultra-low cement or cement-free refractory castables are used for on-site wrapping.
6.Refractory materials for flues and chimneys
The flue lining is usually built with clay bricks, or with prefabricated blocks of refractory castables, which can be hung or poured on site, and sometimes with refractory spray coatings. Red brick or concrete chimneys are built with refractory bricks in high temperature areas. Metal chimneys are welded with metal anchor nails on the inner wall, and sometimes with metal mesh. Lightweight refractory castables or refractory spray coatings are used as linings, which are easy to construct, have strong integrity, and have a long service life.
