What are the refractories used in furnaces?
Heat treatment temperature of the reheating furnace is not high, generally its service temperature is lower than 1300℃.
For reheating furnace lining, usually we use Al-Si refractory materials which contains alumina 36-75%.
The reheating furnace is used for bloom, continuous casting, small steel ingot to meet the temperature needed for hot rolling of thermal equipment. Reheating furnace mainly includes pushing-steel reheat furnace, walking beam furnace and so on.
Walking beam furnace is one type of continuous heating furnace. Its main characteristic is use walking beam hearth (walking beam) to drive furnace charge in the furnace run forward, instead of pushing machine after the furnace charge by running forward.
Each part of reheating furnace temperature usually remains nearly constant, which can be divided into low temperature zone, medium temperature zone and high temperature zone, its temperature is 800 ~ 900 ℃, 900 ~ 1200 ℃, and 1200 ~ 1300℃.
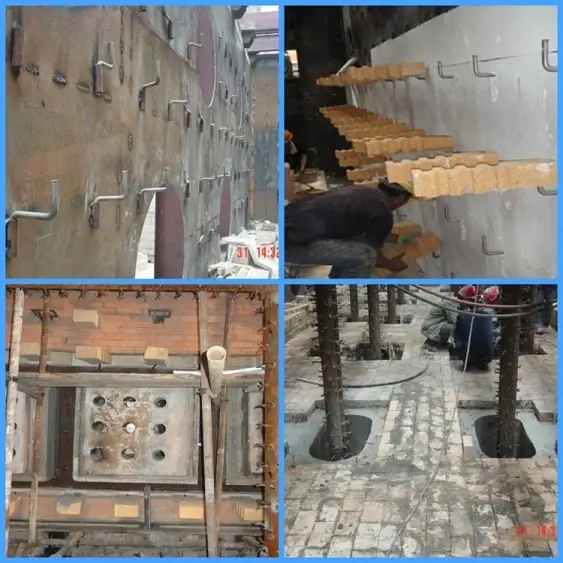
- Plastic refractory(Al2O340%~45%) is used for charging side, exit side, pre-heat period, soaking period and heating period of top, etc. Plastic refractory(Al2O370%) is used for burner parts.
- Mullite anchor brick (Al2O360% & Al2O380%) is used for pre-heat period, soaking period, heating period of top and other fields.
- Clay anchor brick is used for loading side barrier, headwall, flue, etc.
- Heat insulation castable is used for pre-heat period, soaking period and heating period of top.
- High aluminum castable and precast block are used in walking beam and heating period of top.
- Low cement combined with high aluminum cement and precast block are used for outlet end wall, and they both use brown fused alumina as aggregate.
- In addition, the reheating furnace also uses insulation board and other kinds of ceramic fiber insulation materials.

Reheating Furnaces Introduction:
Reheating Furnaces are used for heating the intermediate products of steel like- ingots, blooms or billets at temperatures around 1000 – 1200C before rolling to give them different shapes of angles, channels, bars, slabs, rods & wires etc.
The reheating furnace is a facility to reheat semifinal steel products, such as slab or bloom, which are hot-rolled to thin steel sheet products. In the operation of the reheating furnace, temperatures vary from a relatively low range of about 900°C up to a very high range exceeding 1300°C.
After cooling, the slab, bloom, or billet must be reheated and “softened” for the next forming operation (such as rolling, forging, or extrusion) by raising its temperature to a range of 1600°F to 2500°F. This process is performed in a reheat furnace, a steel structure protected internally by refractory materials.
The reheat furnace application is a critical part of the steel making process. Based on two different operations, continuous and batch, the reheat furnaces can vary in length, capacity, width, and thermal profile. Based on the furnace conditions, each will have a specific refractory design and configuration to maximize success. In addition, each reheat furnace will have specific technical refractory challenges to overcome in order to reach and operate at maximum efficiency. Once the refractory challenges are identified, a solution can be implemented.
Types of Reheat Furnaces
1.Continuous Operation Reheat Furnaces
- Walking Beam
- Pusher
- Rotary Hearth
2.Batch Reheat Furnace
- Car Bottom
- Stationary Solid Hearth
The purpose of Reheat Furnaces
The reheat furnace brings the cold steel to the correct temperature for rolling. Temperature measurements here allow for optimised heating trajectories, providing considerable energy savings. Monitoring also ensures temperature uniformity and consistent product quality, reducing wastage.
Refractories play a very vital role In any integrated steel plant from the stage of coke making to the finished products. With the higher competition In the present world to make steel at cheap and competitive rates. In the operation of the reheating furnace, temperatures vary from a relatively low range of about 900°C up to a very high range exceeding 1300°C.
The modern steel technology requires ever higher quality refractories, which guarantee low specific consumption. Refractories for reheating furnaces play a key role in containing energy consumption and in improving the efficiency of the reheating furnace.
FAQ:
What is the efficiency of a reheating furnace?
The energy efficiency of reheating furnace is usually defined as increase of steel stock heat content when heated from 10 deg C to 1200 deg C divided by the fuel energy (latent heat plus sensible heat) used for it.
What is the combustion of a reheating furnace?
The combustion air cycles between two sets of path-ways in the burner. It enters through one set and picks up heat from the regenerator material in the burner. The combustion product gases exit through the other set and heats up the regenerator material to high temperature.
What is the temperature control of a reheat furnace?
The purpose of a slab reheating furnace is to heat steel slabs to a suitable temperature profile (around 1250°C) before entering to hot rolling phase. The reheating furnace is divided in zones, each zone being controlled independently.
Learn what refractory materials are used in reheating furnaces. What’s more, learn reheating furnace types and the purpose of reheating furnace. If youare interested in other furnace refractory products, welcome to visit our factory.
